Before the Gulf War, the Defense Intelligence Agency assessed that Iraq’s ground forces possibly had chemical mines.[305] This assessment was based on two events. In the first, a Canadian soldier assigned to a UN peacekeeping force after the Iran-Iraq War thought he identified a mine that Iraq had filled with chemical warfare agent. The mine was in an Iraqi conventional minefield along the Iran-Iraq border. It was recovered, however, and positively identified as a conventional mine.[306] The second circumstance that caused concern in the US intelligence community began with an explosives shortage in Italy in the mid-1980s that led to production of mine bodies, which were left unfilled. There were concerns in the US that these mine bodies would be filled with chemical warfare agents by nations such as Iraq, since Iraq’s forces used many Italian-produced mines.[307] So far, this has proved to be unfounded, as post-war inspection and destruction of chemical weapons by UNSCOM revealed no Iraqi chemical mines.[308]
After the war, over 3.5 million mines were collected inside Kuwait and destroyed.[309] See Table 2 for a list of the mines found in the Iraq’s minefields, none of which were chemical. Additionally, of the many captured and translated Iraq’s documents, none addressed chemical mines, except for theoretical discussions.[310] One of Iraq’s captured engineering publications discusses clearing an area of enemy chemical mines, using a US M21 chemical mine as an example.[311]
Table 2. Ordnance (landmine) employment by Iraq’s forces[312]
|
|
|
| Belgium | PRB M409/(anti-personnel) | Simple pressure |
| United Kingdom | Bar Mine (anti-tank) | L89 Single impulse |
| China | Type 69 (plastic)/(anti-personnel) Type 72 (plastic)/(anti-personnel) Type 76 (plastic)/(anti-personnel) PMN (anti-personnel) |
Blast Resistant Simple Pressure Simple Pressure Simple Pressure |
| Czechoslovakia | PT-MI-BA-III/(anti-tank) | Simple Pressure |
| France | MI AC HPD F-2/(anti-tank) | Magnetic |
| Italy | Valmara VS 1.6/(anti-personnel) Valmara VS 2.2 (anti-personnel) Valmara VS 50/ (anti-personnel) |
Blast Resistant Blast Resistant Blast Resistant |
| Egyptian/Spanish | Valmara 59/ (anti-personnel) (Daisy-Chained) Valmara 69 (anti-personnel) (Daisy-Chained) P-40 (anti-personnel) VAR/IG Illumination Mine VS-T Illumination Mine |
Simple Pressure/Trip Wire
Simple Pressure/Trip Wire
Trip Wire Trip Wire/Pressure Trip Wire/Pressure |
| Iraq | P-25/(anti-personnel) | Trip Wire |
| Jordan | PRB-05/(anti-tank) | Single Impulse |
| USSR | TM 46 (anti-tank) TM 57 (anti-tank) TM 62M (anti-tank) |
Simple Pressure Blast Resistant Blast Resistant |
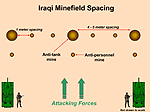
Iraq’s engineers strictly implemented their doctrine for mine laying operations. A US expert on foreign mines stated that he felt very safe in an Iraqi minefield due to the discipline of Iraq’s engineers in following doctrine. Minefield density was consistent and followed the pattern shown in Figure 20 (also see Figures 21 and 22).
Figure 20. Representative Iraqi minefield layout
Figure 22. Iraqi mines in Kuwait.
Three anti-personnel mines are placed one meter from an anti-tank mine, facing the enemy. Each anti-tank mine is separated by four to five meters. Iraq consistently followed this doctrine during the Gulf War across the entire 400 kilometers of minefields. After traveling 300 kilometers of this front, the US expert, looking for signs of booby traps or chemical mines, found none. According to this expert, Iraq followed their doctrine explicitly, and any inclusion of chemical mines would be inconsistent with that doctrine. There would not be unique events of a few chemical mines interspersed among the 3.5 million conventional mines.
Lastly, it was one of his colleague’s expert opinion that chemical mines are "a dumb way to disperse chemicals."[313]
| First Page | Prev Page | Next Page |